Cinebench - R15 score 867 cb with a i7-7700K
Thursday, 01 January 1970 07:00 | Update at null
Media Gallery
Screenshot
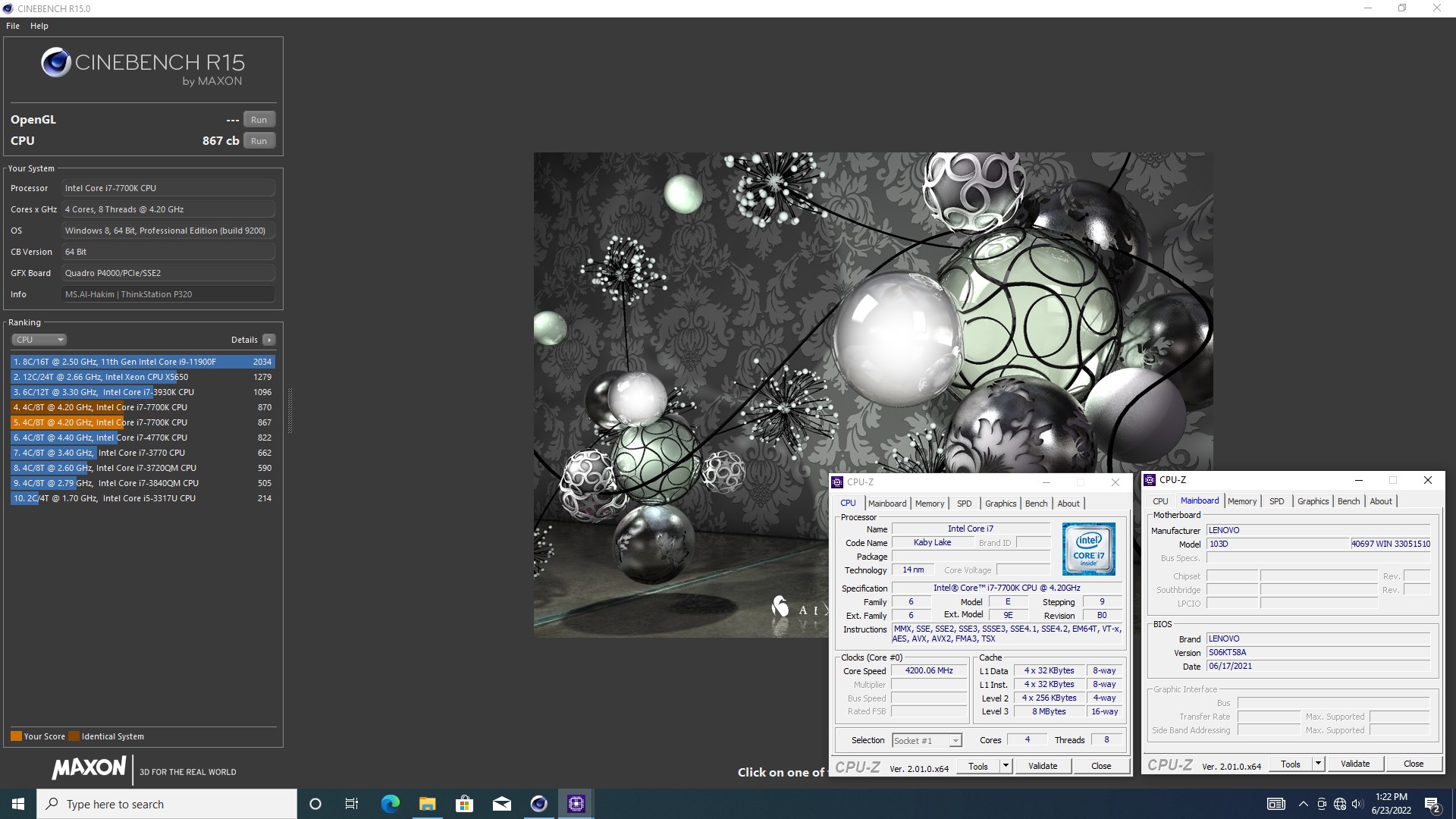
Device, Setup, etc

URL
https://hwbot.org/submission/5024396https://www.facebook.com/hakimnu.id/posts/3314326105466696
Information Detail
Hardware: Intel Core i7 7700K
Specs:CPUID : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700K CPU @ 4.2GHz
Architecture : x86
Codename : Kaby Lake
L3 Cache : 8MB
Clock : 4.2GHz - 4.5GHz
Core/Thread : 4/8
TDP : 91W
Technology : 14nm
Socket : LGA1151
IGPU : Intel HD Graphics 630
See more specification...
Software: Cinebench - R15
Score: 867 cb
About: Cinebench - R15Cinebench R15 is one of the most popular CPU and GPU benchmarks developed by Maxon, the creator of CINEMA 4D software. Released at a time when quad-core processors were becoming commonplace, Cinebench R15 quickly became the standard tool for measuring the rendering performance of various types of desktop and laptop processors. This benchmark simulates the process of rendering photorealistic 3D graphics using the CINEMA 4D engine and assigns a score based on how quickly the CPU can complete the task.
In multi-core testing, Cinebench R15 utilizes all available threads and cores on the processor to render a complex scene consisting of over 300,000 polygons. This scene includes area lighting, soft shadows, sharp and blurry reflections, procedural textures, and anti-aliasing. All these elements are designed to place high stress on the entire CPU processing system, creating an environment that closely resembles real-world scenarios in digital content production or professional rendering.
Cinebench R15 scores are measured in “points” (pts), where higher numbers indicate better performance. This benchmark is ideal for evaluating rendering capabilities, multitasking performance, and overall processor efficiency, especially in applications that utilize multiple cores, such as Blender, Adobe Premiere, or CAD software.
Although Cinebench R15 has been replaced by newer versions like R20 and R23, Cinebench R15 is still widely used today due to its broad compatibility, lightweight execution, and consistent results. Especially for reviewers and users looking to compare processors across generations, R15 remains an important benchmark in the world of hardware and PC enthusiasts.
The Intel Core i7-7700K, launched in early 2017, is a high-performance desktop processor from the 7th generation Kaby Lake family. Built on the 14nm process, the i7-7700K features 4 physical cores and 8 threads, thanks to Hyper-Threading Technology, and is targeted at enthusiasts, gamers, and power users. It operates at a base frequency of 4.2 GHz and can boost up to 4.5 GHz via Intel Turbo Boost, delivering excellent single-threaded performance one of the highest at the time of its release.
As part of Intel’s “K” series, the Core i7-7700K has an unlocked multiplier, making it ideal for overclocking on compatible Z-series motherboards. However, with a TDP of 91W, the processor demands an effective cooling solution, especially when overclocked beyond its stock speeds. Users typically pair this CPU with aftermarket air or liquid coolers to ensure thermal stability under heavy workloads or gaming sessions.
The processor includes Intel HD Graphics 630, which supports 4K output at 60Hz and is sufficient for basic tasks like web browsing, video playback, and office work. However, for serious gaming or GPU-accelerated workloads, a discrete graphics card is still necessary, especially when paired with a high-refresh-rate monitor or demanding software.
In terms of real-world performance, the i7-7700K remains capable even today for 1080p and 1440p gaming, general productivity, and creative tasks. It delivers solid frame rates in many modern titles when used with a modern GPU, and it handles applications like Adobe Photoshop, Premiere Pro, and coding environments reasonably well. However, due to its limited core count by today’s standards and lack of PCIe 4.0 support, it has started to show its age in multi-threaded and next-gen workloads.
Despite being surpassed by newer Intel and AMD CPUs with more cores and better efficiency, the i7-7700K still holds value in many mid-range desktop setups, especially for users who already own an LGA 1151 system and want to maximize performance without a full platform upgrade.
* Not Avaiable
