Comparing: AMD E1-1200 vs Intel Core i9 11900F
In this comparison, we analyze two Processors: AMD E1-1200 and Intel Core i9 11900F, using synthetic benchmark tests to evaluate their overall performance. This side-by-side comparison helps users understand which hardware delivers better value, speed, and efficiency based on standardized testing. Whether you're building a new system or upgrading an existing one, this benchmark-driven evaluation offers valuable insights to guide your decision.
Specification Comparison Table
This specification comparison presents technical details of several devices or components to help you understand the key differences between each option. Use this table as a reference to determine which device best suits your needs.
| Specification | AMD E1-1200 | Intel Core i9 11900F |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | x86 | x86 |
| Technology | 40 nm | 14 nm |
| Clock | 1.4 GHz - - | 2.5 GHz - 5.2 GHz |
| Core/Thread | 2 / 2 | 8 / 16 |
| Segmen | Mobile | Desktop |
Submission Comparison Table
This submission comparison table displays the number and details of benchmark data submissions from various devices or components. This information helps you understand the performance based on the benchmarks that have been tested, as well as providing an overview of the consistency and popularity of the available benchmark results.
| No. | Benchmark Software | AMD E1-1200 | Intel Core i9 11900F |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cinebench - R15 |
44 cb |
2034 cb |
Submission Comparison Chart
This chart visualizes the benchmark scores comparison between two hardware devices based on submitted data.
Media Gallery
A collection of photos of tested hardware. These images can help you identify the physical form, model, and variant of the hardware in question. These photos are from our own documentation, and if they are not available we may not be able to document them.
About Hardware AMD E1-1200
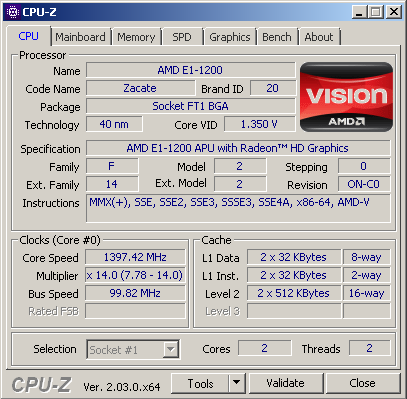
Released in 2012 as part of the Brazos 2.0 family, the AMD E1-1200 is a power-efficient processor aimed at entry-level laptops. It has a 2 core and 2 thread configuration with a fixed clock speed of 1.4 GHz, with no support for Turbo Core technology. Built with a 40nm fabrication process, the E1-1200 has a TDP value of 18 watts-efficient enough for portable devices that emphasize low power consumption and longer battery life. Despite its limited performance, the E1-1200 was a popular choice in its day thanks to its affordable price and ability to handle light computing needs.
One of the main advantages of the AMD E1-1200 is the integrated Radeon HD 7310 GPU, which offers better graphics performance than Intel's entry-level graphics solutions at the time. This GPU has the ability to play HD resolution videos smoothly, as well as run light games such as Counter Strike 1.6, Plants vs Zombies, or other casual games with minimum graphics settings. That said, this combination of CPU and GPU is not intended for heavy-duty work such as video editing, 3D rendering, or modern gaming. Overall performance is more optimal when used for tasks such as browsing, streaming videos, accessing social media, typing documents, as well as basic office applications.
However, it should be noted that the AMD E1-1200 is less suitable for heavy multitasking, especially in modern operating systems like Windows 10. With a low clock speed and no Boost feature, users may experience lag or limitations when opening multiple applications at once. In tests using the HP 1000 1b05au laptop, this processor was paired with 4GB DDR3 single channel RAM (2 DIMM slots) and tested on Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10 operating systems. The results show that the most optimal performance is achieved on Windows 7 or Windows 8, while in Windows 10 the system tends to be slow although it can still be used for basic needs. As such, the AMD E1-1200 can still be relied upon as a power-efficient and inexpensive solution for users with very light computing needs.
Hardware Detail:
Device: HP 1000 1b05au
RAM: 4GB DDR3 Single Channel 2 DIMM
OS: Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10
Wednesday, 26 December 2012 14:27:36 | Update: 1 month ago
About Hardware Intel Core i9 11900F
The Intel Core i9-11900F, launched in 2021, is a high-end desktop processor from the 11th generation Rocket Lake family. Featuring 8 cores and 16 threads, this CPU is built for users who demand strong single-core performance in tasks such as gaming, creative workloads, and professional applications. With a base clock speed of 2.5 GHz and a boost clock up to 5.2 GHz via Intel Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0, the i9-11900F delivers fast responsiveness and excellent performance in lightly threaded scenarios.
Manufactured on the 14nm process, the i9-11900F introduces architectural improvements over its predecessor, including a significant IPC (Instructions Per Cycle) gain, thanks to the new Cypress Cove core design. However, despite these gains, the reliance on the older 14nm node leads to higher power consumption and lower efficiency compared to AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series built on 7nm technology—especially in sustained multi-threaded workloads.
As an “F” series processor, the i9-11900F lacks integrated graphics, meaning it requires a dedicated GPU to operate. This makes it a better fit for gaming PCs or professional workstations that already include a discrete graphics card. While this may not be ideal for users seeking basic systems without a GPU, it allows Intel to price the CPU more competitively.
In benchmarks and real-world performance tests, the Core i9-11900F excels in gaming, offering frame rates comparable to top-tier CPUs when paired with a modern graphics card. It also performs well in productivity tasks such as photo editing, software development, and video rendering—though users working with highly threaded applications might benefit more from CPUs with higher core counts.
Overall, the Intel Core i9-11900F is a solid choice for enthusiast builders, gamers, and users looking for top-tier single-core performance, but it may not be the most efficient option for heavy multitasking or rendering workloads when compared to newer multi-core CPUs.
Monday, 20 June 2022 07:37:04 | Update: 1 month ago