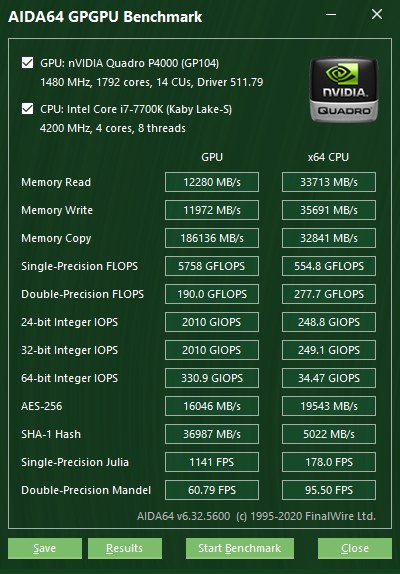
AIDA64 GPGPU Benchmark - Single Precision FLOPS score 554.8 GFLOPS with a i7-7700K
Wednesday, 22 February 2023 00:25 | Update at 2 years ago
Media Gallery
Screenshot
Device, Setup, etc

URL
https://bit.ly/3Tx06OpInformation Detail
Hardware: Intel Core i7 7700K
Specs:CPUID : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700K CPU @ 4.2GHz
Architecture : x86
Codename : Kaby Lake
L3 Cache : 8MB
Clock : 4.2GHz - 4.5GHz
Core/Thread : 4/8
TDP : 91W
Technology : 14nm
Socket : LGA1151
IGPU : Intel HD Graphics 630
See more specification...
Software: AIDA64 GPGPU Benchmark - Single Precision FLOPS
Score: 554.8 GFLOPS
About: AIDA64 GPGPU Benchmark - Single Precision FLOPSAIDA64 GPGPU Benchmark is a benchmarking feature available within the AIDA64 application, specifically aimed at measuring GPU parallel computing performance through OpenCL technology. It can be accessed through the Tools | GPGPU Benchmark menu, and is designed to evaluate the ability of various GPU devices to run compute-intensive workloads. AIDA64 supports testing up to 16 GPUs simultaneously, including combinations of AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA, whether in discrete GPU (dGPU), integrated GPU (APU), or multi-GPU systems such as SLI and CrossFire.
One of the key tests in this benchmark is Single Precision FLOPS, which measures the GPU's ability to perform 32-bit floating point operations (FP32). This test is important because many modern applications-especially in graphics, physics, AI, and video processing-rely on FP32 as the basis for key calculations. The resulting score in GFLOPS (Giga Floating Point Operations per Second) indicates how fast the GPU can complete a large number of single-precision mathematical calculations in parallel.
This benchmark not only provides a benchmark of general GPU computing performance, but is also an important indicator for GPGPU-based workloads (General Purpose GPU Computing). By relying on the OpenCL standard, this test is cross-platform and able to measure the performance of various GPU vendors in a fair and open manner. Even systems with mixed or hybrid GPUs can be thoroughly tested as long as they are recognized as computing units by the OpenCL driver.
The AIDA64 GPGPU Benchmark is particularly useful for professional users, parallel software developers, and technology enthusiasts who want to assess the power of their GPU in a computational context, not just in graphics rendering. With support for multi-GPU configurations and detailed results, this benchmark is a reliable tool for evaluating hardware performance in demanding tasks that require precision and high throughput.
The Intel Core i7-7700K, launched in early 2017, is a high-performance desktop processor from the 7th generation Kaby Lake family. Built on the 14nm process, the i7-7700K features 4 physical cores and 8 threads, thanks to Hyper-Threading Technology, and is targeted at enthusiasts, gamers, and power users. It operates at a base frequency of 4.2 GHz and can boost up to 4.5 GHz via Intel Turbo Boost, delivering excellent single-threaded performance one of the highest at the time of its release.
As part of Intel’s “K” series, the Core i7-7700K has an unlocked multiplier, making it ideal for overclocking on compatible Z-series motherboards. However, with a TDP of 91W, the processor demands an effective cooling solution, especially when overclocked beyond its stock speeds. Users typically pair this CPU with aftermarket air or liquid coolers to ensure thermal stability under heavy workloads or gaming sessions.
The processor includes Intel HD Graphics 630, which supports 4K output at 60Hz and is sufficient for basic tasks like web browsing, video playback, and office work. However, for serious gaming or GPU-accelerated workloads, a discrete graphics card is still necessary, especially when paired with a high-refresh-rate monitor or demanding software.
In terms of real-world performance, the i7-7700K remains capable even today for 1080p and 1440p gaming, general productivity, and creative tasks. It delivers solid frame rates in many modern titles when used with a modern GPU, and it handles applications like Adobe Photoshop, Premiere Pro, and coding environments reasonably well. However, due to its limited core count by today’s standards and lack of PCIe 4.0 support, it has started to show its age in multi-threaded and next-gen workloads.
Despite being surpassed by newer Intel and AMD CPUs with more cores and better efficiency, the i7-7700K still holds value in many mid-range desktop setups, especially for users who already own an LGA 1151 system and want to maximize performance without a full platform upgrade.
* Not Avaiable
