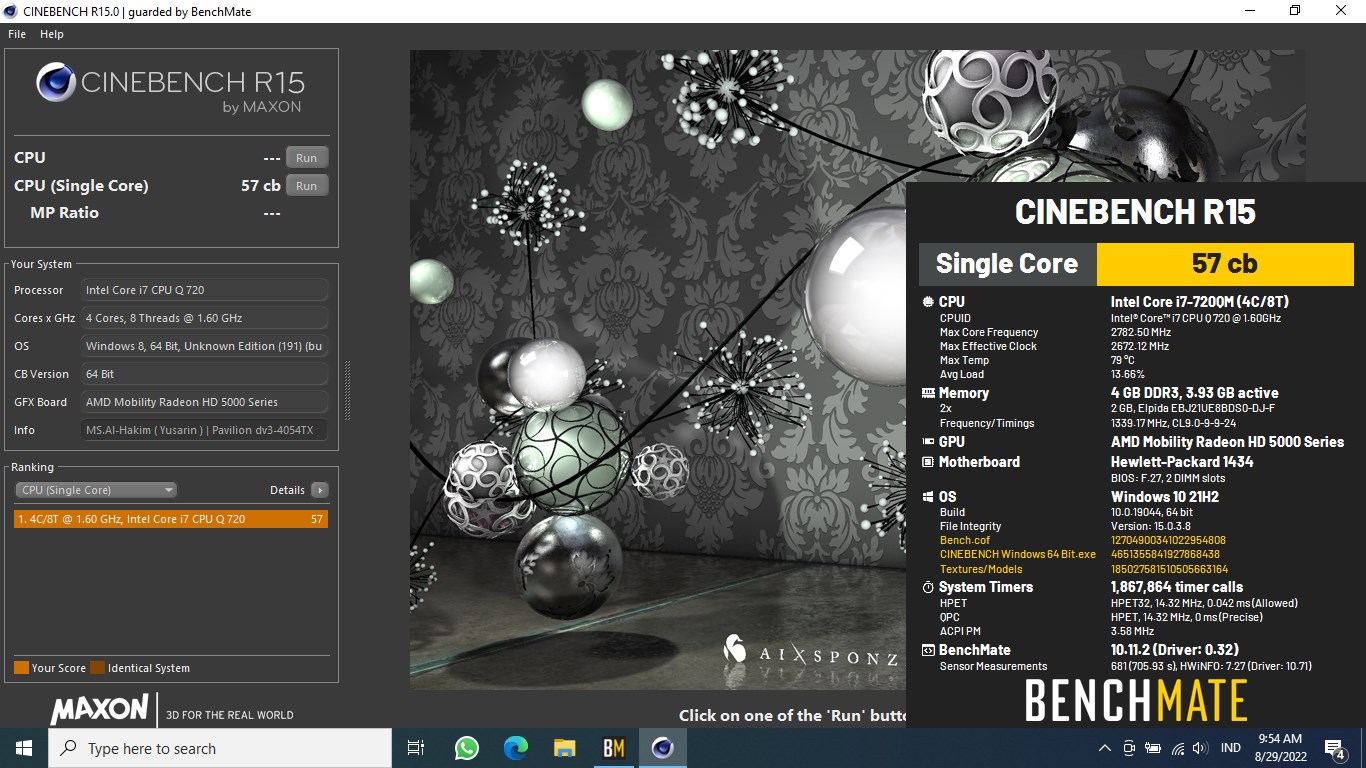
Cinebench - R15 Single Core score 57 cb with a i7-720QM
Thursday, 01 January 1970 07:00 | Update at null
Media Gallery
Screenshot
Device, Setup, etc

URL
https://www.facebook.com/hakimnu.id/posts/3332688523630454Information Detail
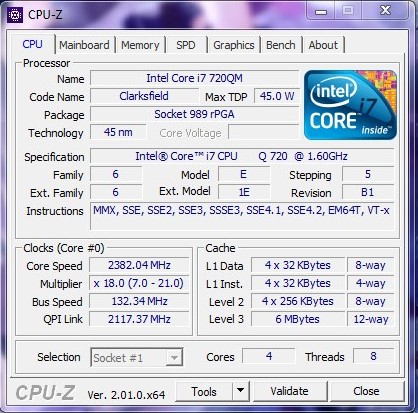
Hardware: Intel Core i7 720QM
Specs:CPUID : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 CPU Q 720 @ 1.60GHz
Architecture : x86
Codename : Clarksfield
L3 Cache : 6MB
Clock : 1.60GHz - 2.80GHz
Core/Thread : 4/8
TDP : 45W
Technology : 45nm
Socket : PGA988
IGPU : -
See more specification...
Software: Cinebench - R15 Single Core
Score: 57 cb
About: Cinebench - R15 Single CoreCinebench R15 Single Core is a testing version of the popular Cinebench R15 benchmark, specifically designed to measure the single-core (single-thread) performance of a processor. This benchmark was developed by Maxon, the company behind the professional 3D software CINEMA 4D, and has become one of the industry standards for testing processor performance in various rendering scenarios.
Unlike multi-core testing, which utilizes all CPU cores, single-core testing uses only one processor core to render the same 3D scene as the multi-core version. This provides a realistic picture of a CPU's ability to handle light to medium workloads, which are still common in everyday applications such as web browsing, document processing, older games, or applications that are not yet optimized for multi-threading.
Cinebench R15 Single Core scores are measured in “points” (pts), where higher values indicate that the processor can complete tasks faster with a single core. This score is crucial because while many modern processors offer multiple cores, per-core performance remains the primary indicator in many real-world scenarios. This test is also highly useful for users seeking to assess CPU architecture efficiency, IPC (Instructions Per Clock), and single-core boost capabilities.
Cinebench R15 Single Core is frequently used by reviewers, overclockers, and professional users to compare performance across generations or between CPU brands. Although Cinebench has released newer versions such as R20 and R23, R15 remains relevant due to its lightweight nature and continued use as a benchmark for basic system performance testing.
The Intel Core i7-720QM, launched in Q3 2009, was one of the first mobile quad-core processors to feature Intel's Nehalem microarchitecture, specifically the Clarksfield variant. Targeted at high-performance laptops, such as gaming machines and mobile workstations, the i7-720QM brought 4 physical cores and 8 threads to the mobile platform, thanks to Hyper-Threading Technology providing a significant boost in multi-threaded workloads like video editing, 3D rendering, and other professional-grade applications. The processor runs at a base clock speed of 1.6 GHz, but it can dynamically increase up to 2.8 GHz using Intel Turbo Boost, depending on thermal headroom and power availability.
Manufactured using a 45nm process, the i7-720QM has a TDP of 45W, which is quite high by today's mobile CPU standards. This thermal demand necessitated more robust cooling solutions in laptops that featured the chip. Unlike modern CPUs, the i7-720QM does not come with integrated graphics, which means systems based on this processor require a dedicated GPU often from AMD or NVIDIA for graphics processing and display output. As such, it was typically paired with mid-to-high-end discrete graphics cards in its time, making it a solid choice for gaming and multimedia laptops in the late 2000s and early 2010s.
While the Core i7-720QM was a powerhouse during its release, its performance and efficiency are significantly outpaced by modern CPUs built on smaller nodes and with higher IPC (Instructions Per Clock). Nevertheless, legacy laptops using the i7-720QM can still be viable for basic computing tasks like web browsing, document editing, or watching videos especially if paired with an SSD upgrade and increased RAM. Users running Windows 10 on such systems may experience some limitations, but with proper optimization and lightweight software, the CPU can still deliver a usable experience in non-demanding environments.
Hardware Detail:
Device: HP Pavilion dv3-4054TX
RAM: 4GB DDR3 Single Channel
OS: Windows 7, Windows 10
* Not Avaiable
